
截止目前,引用Bioss产品发表的文献共33241篇,总影响因子162891.42分,发表在Nature, Science, Cell以及Immunity等期刊的文献共125篇,合作单位覆盖了清华、北大、复旦、华盛顿大学、麻省理工学院、东京大学以及纽约大学等上百所国际研究机构。
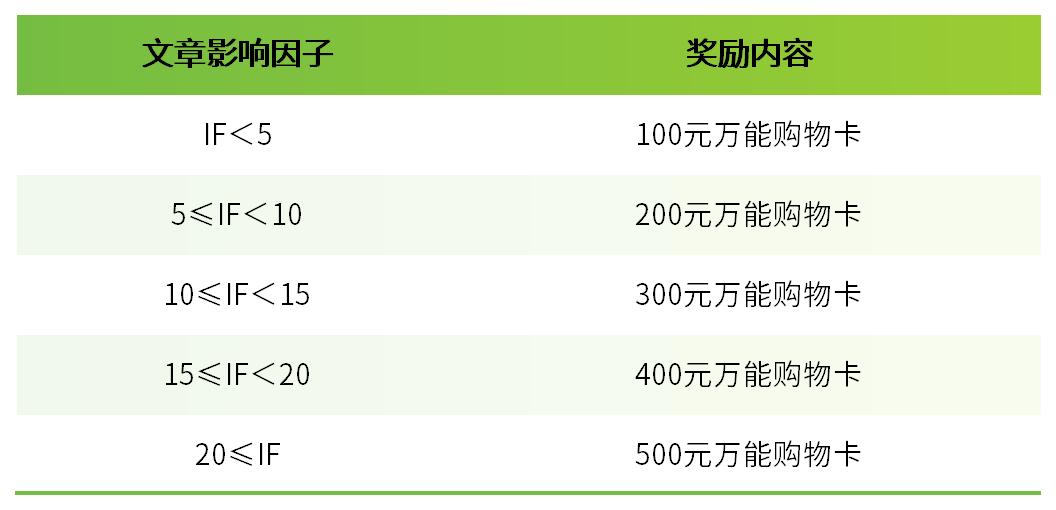
我们每月收集引用Bioss产品发表的文献。若您在当月已发表SCI文章,但未被我公司收集,请致电Bioss,我们将赠予现金鼓励,金额标准请参考“发文章 领奖金”活动页面。
本文主要分享引用Bioss产品发表文章至Cell, Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy, Cell Metabolism, Advanced Materials, nature biomedical engineering, Bioactive Materials, Nature Aging, Nucleic Acids Research, ACS Nano等期刊的11篇IF>15的文献摘要,让我们一起欣赏吧。
CELL [IF=45.5]

文献引用产品:
作者单位:美国波士顿儿童医院
摘要:The composition and organization of the cell surface determine how cells interact with their environment. Traditionally, glycosylated transmembrane proteins were thought to be the major constituents of the external surface of the plasma membrane. Here, we provide evidence that a group of RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) is present on the surface of living cells. These cell-surface RBPs (csRBPs) precisely organize into well-defined nanoclusters enriched for multiple RBPs and glycoRNAs, and their clustering can be disrupted by extracellular RNase addition. These glycoRNA-csRBP clusters further serve as sites of cell-surface interaction for the cell-penetrating peptide trans-activator of transcription (TAT). Removal of RNA from the cell surface, or loss of RNA-binding activity by TAT, causes defects in TAT cell internalization. Together, we provide evidence of an expanded view of the cell surface by positioning glycoRNA-csRBP clusters as a regulator of communication between cells and the extracellular environment.
Signal Transduction and
Targeted Therapy [IF=40.8]

文献引用产品:
作者单位:四川大学华西医院
Cell Metabolism [IF=27.7]

文献引用产品:
摘要:Metabolic-dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH) remains a major health challenge. Herein, we identify sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase 3 (SMPD3) as a key driver of hepatic ceramide accumulation through increasing sphingomyelin hydrolysis at the cell membrane. Hepatocyte-specific Smpd3 gene disruption or pharmacological inhibition of SMPD3 alleviates MASH, whereas reintroducing SMPD3 reverses the resolution of MASH. Although healthy livers express low-level SMPD3, lipotoxicity-induced DNA damage suppresses sirtuin 1 (SIRT1), triggering an upregulation of SMPD3 during MASH. This disrupts membrane sphingomyelin-ceramide balance and promotes disease progression by enhancing caveolae-dependent lipid uptake and extracellular vesicle secretion from steatotic hepatocytes to exacerbate inflammation and fibrosis. Consequently, SMPD3 acts as a central hub integrating key MASH hallmarks. Notably, we discovered a bifunctional agent that simultaneously activates SIRT1 and inhibits SMPD3, which shows significant therapeutic potential in MASH treatment. These findings suggest that inhibition of hepatic SMPD3 restores membrane sphingolipid metabolism and holds great promise for developing novel MASH therapies.
Advanced Materials [IF=27.4]

文献引用产品:
摘要:Immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) therapy has achieved remarkable benefits in the treatment of malignant tumors, but the clinical response rates are unsatisfied due to the low tumor immunogenicity and the abundant immunosuppressive cells. Herein, a plasma membrane targeted photodynamic nanoagonist (designated as PMTPN) is developed to potentiate ICB therapy by initiating tumor cell pyroptosis and depleting infiltrating B cells. PMTPN is composed of a rationally designed chimeric peptide sequence loaded with Bruton's tyrosine kinase inhibitor (Ibrutinib). Notably, PMTPN is capable of sequentially targeting tumor and tumor cell membrane to trigger immunogenic pyroptosis and cause overwhelming release of cytokines, promoting dendritic cells maturation, and cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) activation. Meanwhile, PMTPN can also deplete infiltrating B cells and reduce the secretion of interleukin-10 to decrease immunosuppressive regulatory T cells and enhance CTLs infiltration. Beneficially, the synergistic immune modulating characteristics of PMTPN potentiate ICB therapy to simultaneously eliminate primary and distant tumors. This study offers a promising strategy to elevate the immunotherapeutic response rate in consideration of the complex immunosuppressive factors.
Nature biomedical
engineering [IF=26.8]

文献引用产品:
摘要:The efficacy of bacteriophages in treating bacterial infections largely depends on the phages’ vitality, which is impaired when they are naturally released from their hosts, as well as by culture media, manufacturing processes and other insults. Here, by wrapping phage-invaded bacteria individually with a polymeric nanoscale coating to preserve the microenvironment on phage-induced bacterial lysis, we show that, compared with naturally released phages, which have severely degraded proteins in their tail, the vitality of phages isolated from polymer-coated bacteria is maintained. Such latent phages could also be better amplified, and they more efficiently bound and lysed bacteria when clearing bacterial biofilms. In mice with bacterially induced enteritis and associated arthritis, latent phages released from orally administered bacteria coated with a polymer that dissolves at neutral pH had higher bioavailability and led to substantially better therapeutic outcomes than the administration of uncoated phages.
Bioactive Materials [IF=18]

文献引用产品:
bs-0195R | CD31 Rabbit pAb | IF
作者单位:中山大学
摘要:The divalent metal cations promote new bone formation through modulation of sensory and sympathetic nervous systems (SNS) activities. In addition, acetylcholine (Ach), as a chief neurotransmitter released by the parasympathetic nervous system (PNS), also affects bone remodeling, so it is of worth to investigate if the divalent cations influence PNS activity. Of note, these cations are key co-enzymes modulating glucose metabolism. Aerobic glycolysis rather than oxidative phosphorylation favors osteogenesis of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), so it is of interest to study the effects of these cations on glucose metabolic pathway. Prior to biological function assessment, the tolerance limits of the divalent metal cations (Mg2+, Zn2+, and Ca2+) and their combinations were profiled. In terms of direct effects, these divalent cations potentially enhanced migration and adhesion capability of MSCs through upregulating Tgf-β1 and Integrin-β1 levels. Interestingly, the divalent cations alone did not influence osteogenesis and aerobic glycolysis of undifferentiated MSCs. However, once the osteogenic differentiation of MSCs was initiated by neurotransmitters or osteogenic differentiation medium, the osteogenesis of MSCs could be significantly promoted by the divalent cations, which was accompanied by the improved aerobic glycolysis. In terms of indirect effects, the divalent cations significantly upregulated levels of sensory nerve derived CGRP, PNS produced choline acetyltransferase and type H vessels, while significantly tuned down sympathetic activity in the defect zone in rats, thereby contributing to significantly increased bone formation relative to the control group. Together, the divalent cations favor bone regeneration via modulation of sensory-autonomic nervous systems and promotion of aerobic glycolysis-driven osteogenesis of MSCs after osteogenic initiation by neurotransmitters.
Bioactive Materials [IF=18]

bs-23103R | Ki-67 Rabbit pAb | IHC
Nature Aging [IF=17]

文献引用产品:
bs-0295D-BF647 | Donkey Anti-Rabbit IgG H&L, BF647 conjugated | IF
SV6000 | 标记服务 | IF
作者单位:德国吕贝克大学
摘要:Blood-borne factors are essential to maintain neuronal synaptic plasticity and cognitive resilience throughout life. One such factor is osteocalcin (OCN), a hormone produced by osteoblasts that influences multiple physiological processes, including hippocampal neuronal homeostasis. However, the mechanism through which this blood-borne factor communicates with neurons remains unclear. Here we show the importance of a core primary cilium (PC) protein–autophagy axis in mediating the effects of OCN. We found that the OCN receptor GPR158 is present at the PC of hippocampal neurons and mediates the regulation of autophagy machinery by OCN. During aging, autophagy and PC core proteins are reduced in neurons, and restoring their levels is sufficient to improve cognitive impairments in aged mice. Mechanistically, the induction of this axis by OCN is dependent on the PC-dependent cAMP response element-binding protein signaling pathway. Altogether, this study demonstrates that the PC–autophagy axis is a gateway to mediate communication between blood-borne factors and neurons, and it advances understanding of the mechanisms involved in age-related cognitive decline.
Nucleic Acids Research [IF=16.6]

文献引用产品:
作者单位:上海交通大学医学院附属仁济医院

文献引用产品:
bs-4916R-APC | CD44 Rabbit pAb, APC conjugated | Flow-Cyt
作者单位:中国科学院生物医学与生物技术研究所
摘要:“Living therapeutic carriers” present a promising avenue for cancer research, but it is still challenging to achieve uniform and durable distribution of payloads throughout the solid tumor owing to the tumor microenvironment heterogeneity. Herein, a living drug sprinkle biohybrid (YB1–HCNs) was constructed by hitching acid/enzyme-triggered detachable nanoparticles (HCNs) backpack on the surface of metabolic oligosaccharide-engineered oncolytic bacteria YB1. Along with the process of tumor penetration by bacterial hypoxia navigation, YB1–HCNs responsively and continuously release HCNs, achieving a uniform distribution of loaded agents throughout the tumor. Upon successive irradiation of laser and ultrasound (US), the HCNs can separately generate type II and type I ROS for superior sono–photodynamic therapy (SPDT), which enables HCNs to synergize with YB1 for a satisfactory therapeutic effect in both superficial normoxic and deep hypoxic regions of the tumor. After a single dose, this efficient combination realized 98.3% primary tumor inhibition rate and prolonged survival of mice for 90 days with no recurrence, further inducing a powerful immunological memory effect to completely suppress tumor rechallenge in cured mice. Such a bacterial hybridization vector enables optimization of the spatial distribution of YB1 and HCNs, providing an innovative strategy to maximize therapeutic outcomes and evoke durable antitumor immunity.
ACS Nano [IF=15.8]

文献引用产品:
作者单位:首都医科大学附属北京友谊医院
